The Gist
- Accuracy through collaboration. AI reliability depends not only on better models but on active user participation that refines and strengthens results.
- UX as a trust engine. Design patterns that clarify, guide, and invite feedback make users partners in improving AI performance.
- From passive to participatory. Forward-thinking UX teams transform users into co-creators, fostering engagement, accuracy, and long-term trust.
The AI revolution is transforming how we work, create and solve problems. Yet, while capabilities continue to advance, a critical challenge persists: AI accuracy. Companies must enlist their users to improve.
This not only helps the models get better, but also engages users in new ways, where they can feel like they are participating in the product's development, which gives them a sense of ownership and investment in the product’s success.
This collaborative approach transforms users from passive consumers into active contributors, creating a virtuous cycle where better user engagement leads to better AI performance, which in turn drives deeper customer satisfaction and customer trust.
Forward-thinking experience teams are pioneering design patterns that make this partnership feel natural and rewarding, turning every interaction into an opportunity for mutual improvement.
Here are 10 proven UX tactics that leading companies are implementing to build trust and improve AI accuracy through thoughtful design.
Table of Contents
- How UX Teams Are Making AI Outputs More Reliable
- UX Design in Digital Customer Experience: CMSWire's Take
- UX Design: The Foundation of Digital Customer Experience
- UX Research and Human-Centered Design
- Designing From the Customer’s Perspective
- Redefining Digital Strategy Around the Screen
- Aligning UX and CX for Lasting Impact
How UX Teams Are Making AI Outputs More Reliable
1. Expectation Setting & Transparency
What it does: Clearly communicates AI’s capabilities, limitations and progress during tasks.
Why it works: Builds trust by avoiding overpromising and keeping users informed.
Example:
- Claude AI — Live progress updates during requests.

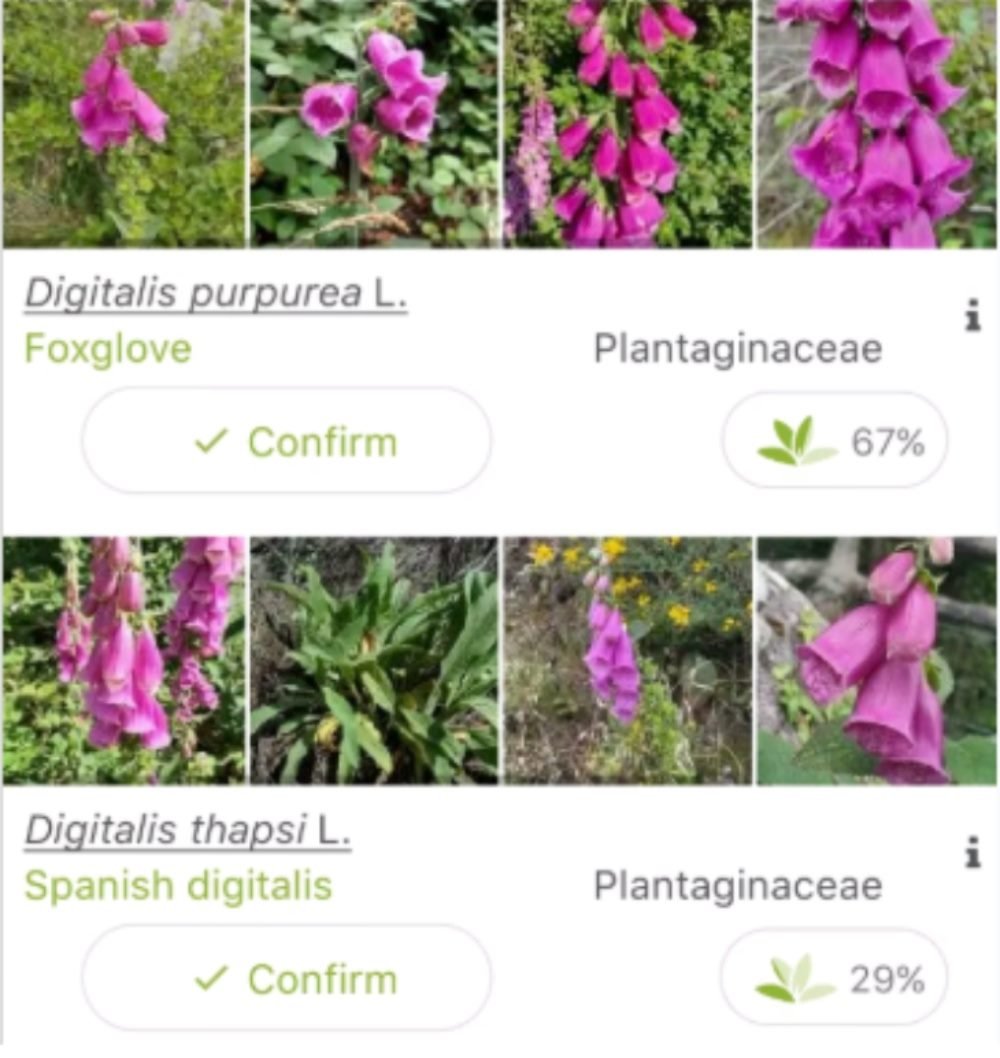
2. Confidence Scores
What it does: Shows how certain the AI is about its outputs, often as percentages or probability bars.
Why it works: Helps users gauge reliability and decide when to verify results.
Example:
- PlantNet — Displays probability percentage for plant matches.
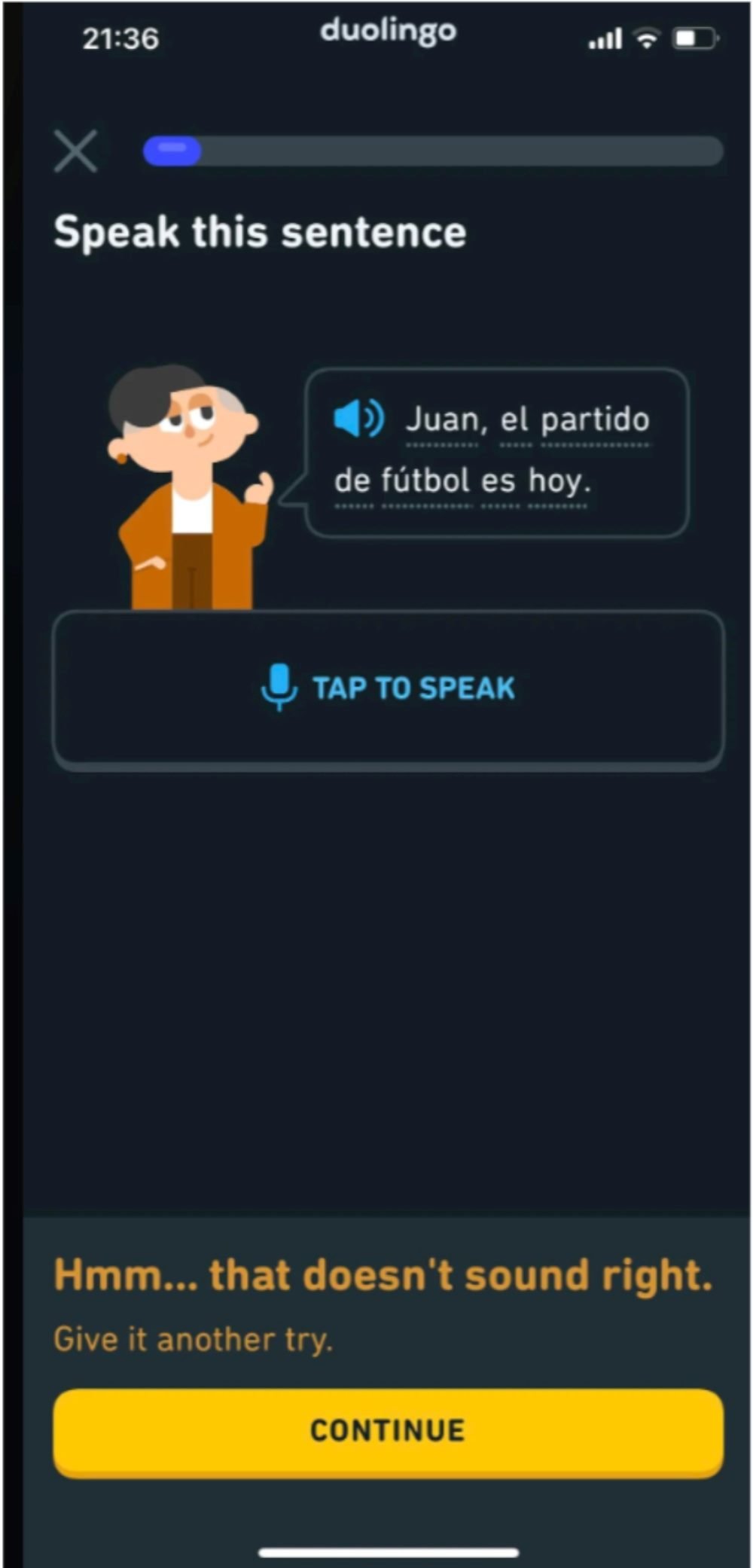
3. Error Prevention via Input Guidance
What it does: Helps users provide better inputs through prompts, hints and validation.
Why it works: Reduces errors before they occur.
Example:
- Duolingo — Microcopy like “Tap the speaker to hear pronunciation.”
4. Graceful Error Recovery
What it does: Responds constructively when AI makes mistakes, allowing quick correction.
Why it works: Maintains trust and flow after misfires.
Example:
- Gmail Smart Compose — Predictions vanish instantly if user types something different.
5. Feedback Collection & Model Improvement
What it does: Captures structured user feedback directly on AI outputs.
Why it works: Turns every interaction into data for improvement.
Example:
- ChatGPT — Thumbs-up/down with comment options.

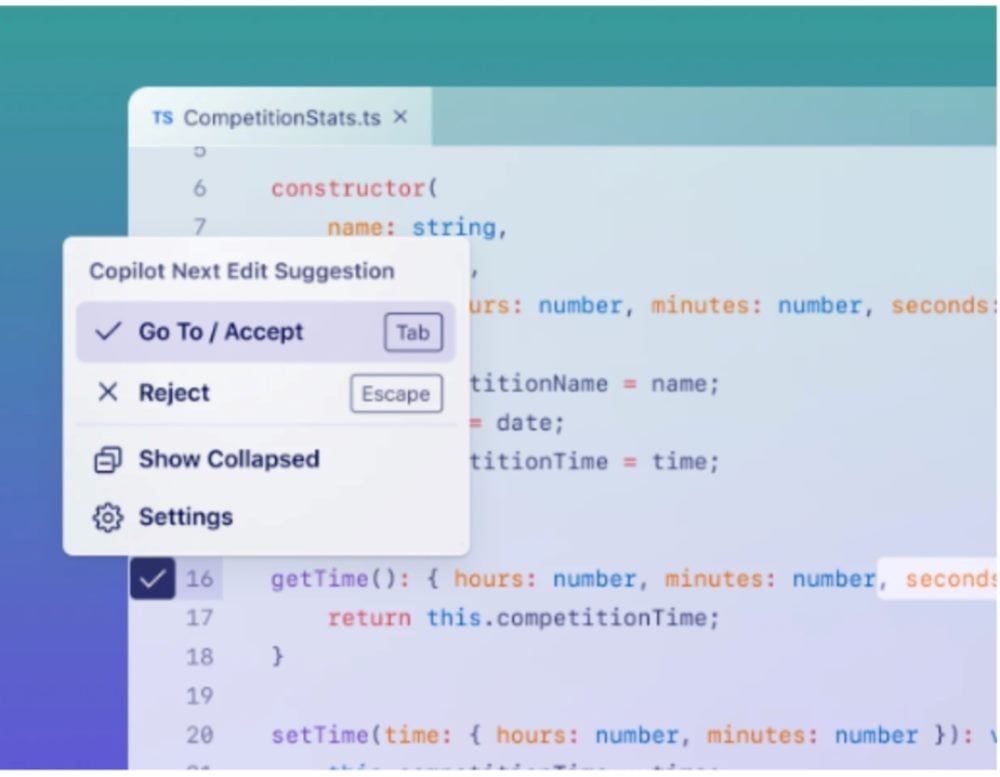
6. User Control & Collaboration
What it does: Gives users clear choices in accepting, rejecting or modifying AI suggestions.
Why it works: Creates a sense of partnership rather than automation overreach.
Examples:
- GitHub Copilot — Multiple options for code suggestions.
- Notion AI — “Improve writing” for easy edits.
7. Progressive Disclosure
What it does: Reveals complex information in manageable steps.
Why it works: Reduces cognitive load while still allowing access to advanced features.
Examples:
- Perplexity AI — Follow-up questions shown one at a time.
- Cisco Virtual Troubleshooter — Sequential diagnostic steps.
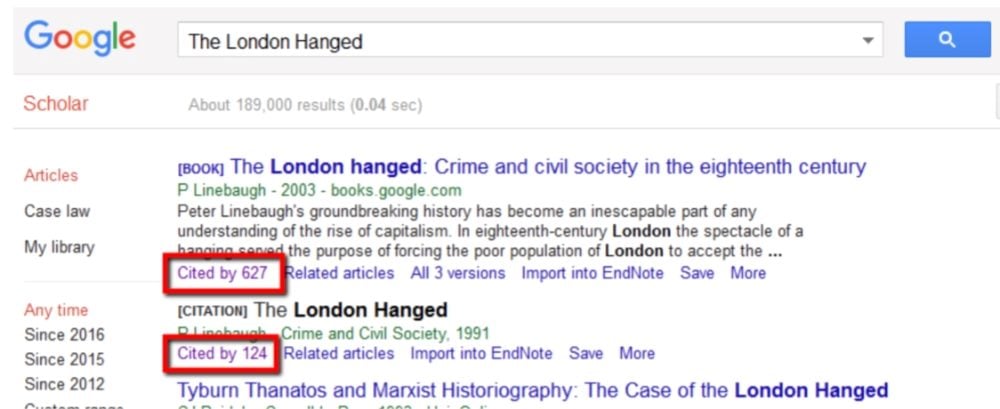
8. Source Attribution & Verification
What it does: Shows where AI’s output came from and allows verification.
Why it works: Builds credibility and supports fact-checking.
Examples:
- Google Scholar — Citation counts and links.
- Perplexity AI — Inline citations linking to sources.
9. Validation Quests
What it does: Prompts users to confirm whether AI solutions worked, sometimes offering rewards or gamified incentives.
Why it works: Collects verified, real-world feedback to improve models.
Example:
- Amazon product reviews — “Was this review helpful?” with Yes/No buttons.
- Stack Overflow — Answer acceptance and helpfulness voting.HTML
10. Personalization & Context Retention
What it does: Adapts AI behavior and recommendations based on past interactions, user preferences, and ongoing conversation history.
Why it works: Reduces repeated errors, surfaces more relevant suggestions, and makes the AI feel attuned to the individual user.
Example:
- Spotify AI DJ — Curates playlists and commentary based on listening history.

The future of AI isn't just about more powerful models. It's about creating human-AI partnerships where uncertainty becomes manageable, errors become learning opportunities, and trust grows through thoughtful design. UX teams that master these patterns today will define how humans and AI collaborate tomorrow.
UX isn't just about aesthetics or functionality; it's becoming the primary lever for AI reliability. The patterns outlined here are already delivering measurable improvements in user trust and AI accuracy. As the field evolves, design will continue shaping AI's trajectory toward transparency, collaboration and genuine user empowerment.
UX Design in Digital Customer Experience: CMSWire's Take
User experience (UX) design sits at the heart of every successful digital customer experience strategy. It bridges the gap between what customers expect and what digital platforms deliver — ensuring every click, tap and scroll feels purposeful, intuitive and satisfying. Below, we explore how UX design serves as the foundation for building trust, loyalty and seamless interactions across digital touchpoints.
UX Design: The Foundation of Digital Customer Experience
User experience design is the operational backbone of digital customer experience, zeroing in on the specific moments when users interact with digital products like websites and apps. While customer experience covers the entire journey, UX focuses on making each digital touchpoint intuitive, accessible and frictionless, which builds trust and loyalty with every interaction, according to industry experts.
UX Research and Human-Centered Design
UX design is rooted in research, blending qualitative and quantitative insights to craft seamless, human-centered experiences. This includes developing personas, prototyping and conducting usability tests to ensure every interaction feels effortless and personal. As outlined in recent analysis, UX design employs methods such as wireframes, visual comps and iterative testing to optimize each digital interaction for clarity and ease of use.
Designing From the Customer’s Perspective
Human-centered design is key to creating digital experiences that feel as effortless as walking into your favorite store, with every need within reach. By prioritizing the customer's perspective from the start, organizations can solve real problems for users and foster trust and loyalty.
Redefining Digital Strategy Around the Screen
Experts now recommend starting with the customer's perspective and reverse-engineering your digital stack from the screen outward, rather than forcing customers to adapt to your org chart. The only center that matters is the customer's screen, where every tap, scroll and hesitation reveals if your strategy is working.
Aligning UX and CX for Lasting Impact
In short, aligning UX and CX strategies helps brands deliver journeys that are not only efficient but also emotionally resonant, turning users into advocates. And remember: nothing says "we care" like a website that just works—no instruction manual required.
Learn how you can join our contributor community.